Native versus cross-platform frameworks to develop accessible apps
It's important to consider accessibility when developing an app. Over 1 billion people in the world have a disability. And 50% of all people use accessibility features on their mobile devices.
A question we are often asked is: "Which framework should I choose to develop an accessible app?"
In this article, we are comparing the pros and cons of Android, iOS, Flutter, React Native and Xamarin. And we added Web equivalents. A conclusion is drawn at the end.
This article has been updated on 30 January 2025 to reflect the new API in Flutter to move focus order.
1. Orientation
Apps should support multiple orientations (portrait and landscape) to ensure users can hold devices in their preferred way.
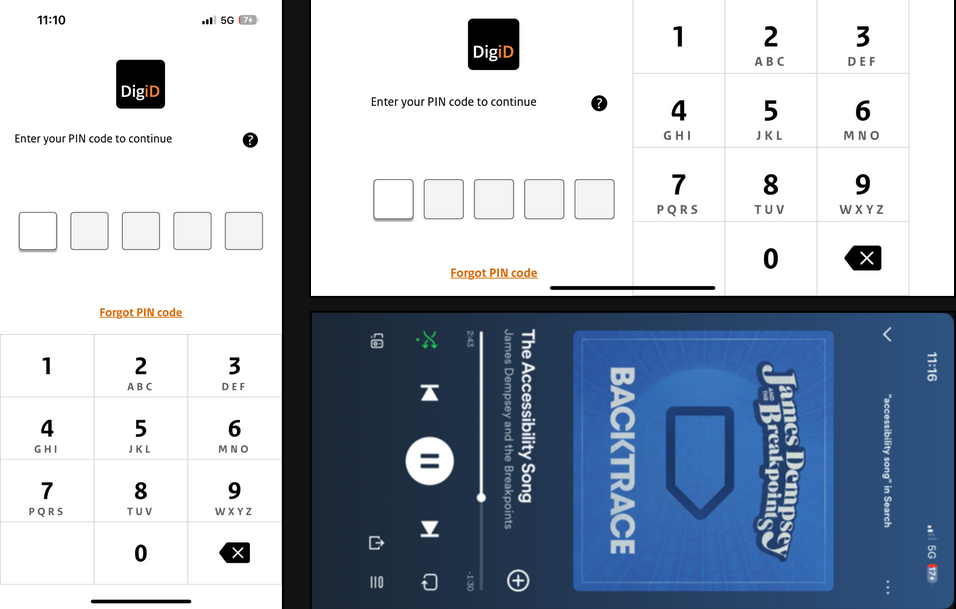

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | android:screenOrientation | All orientations supported by default | |
| iOS | UISupportedInterfaceOrientations | 'Upside Down' disabled by default | |
| Flutter | setPreferredOrientations | Flexible | |
| React Native | expo-screen-orientation or native | Flexible | |
| Xamarin | Device Orientation or native | Flexible | |
| Web | @media query | Extensive |
2. Text scaling
Apps should support text scaling, to ensure users can read text in the font size they need.
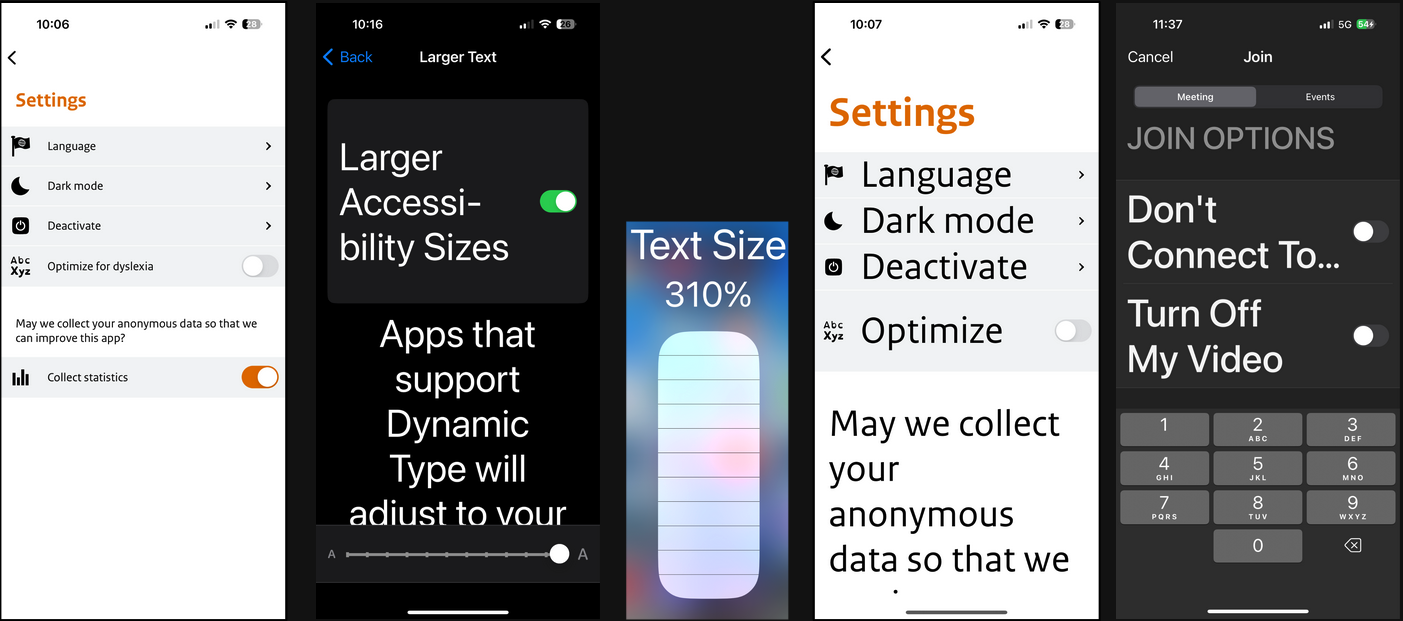

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | Scale-independent Pixels (sp) | Scales automatically | |
| iOS | UIFontMetrics | Write scaling implementation | |
| Flutter | fontSize | Scales automatically | |
| React Native | fontSize | Scales automatically | |
| Xamarin | SetEnableAccessibilityScalingForNamedFontSizes | Write scaling implementation | |
| Web | (r)em unit / Browser zoom | Scales automatically |
3. Contrast
Apps should have sufficient contrast, to ensure users can read text and distinguish interface elements.
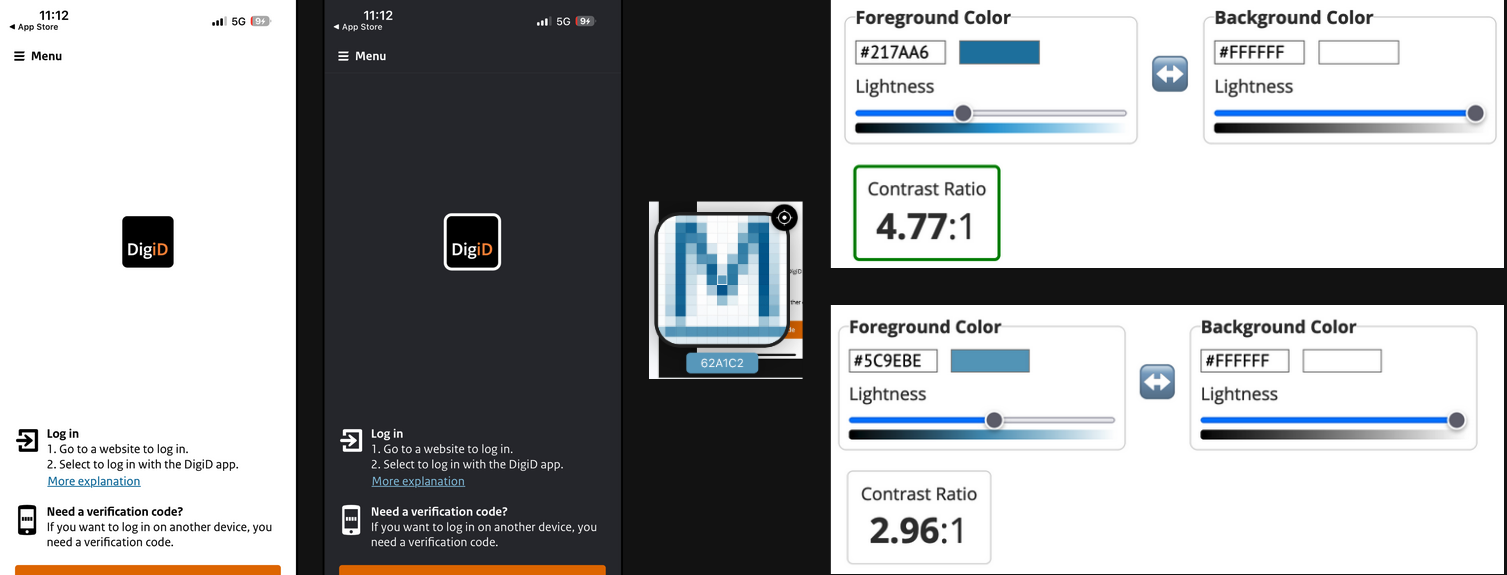

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | Color | ||
| iOS | Color | Built-in high contrast support | |
| Flutter | Color | ||
| React Native | Color | ||
| Xamarin | Color | ||
| Web | <color> |
4. Name
Apps should provide an accessible name for interactive elements, to ensure users of assistive technologies can identify them.
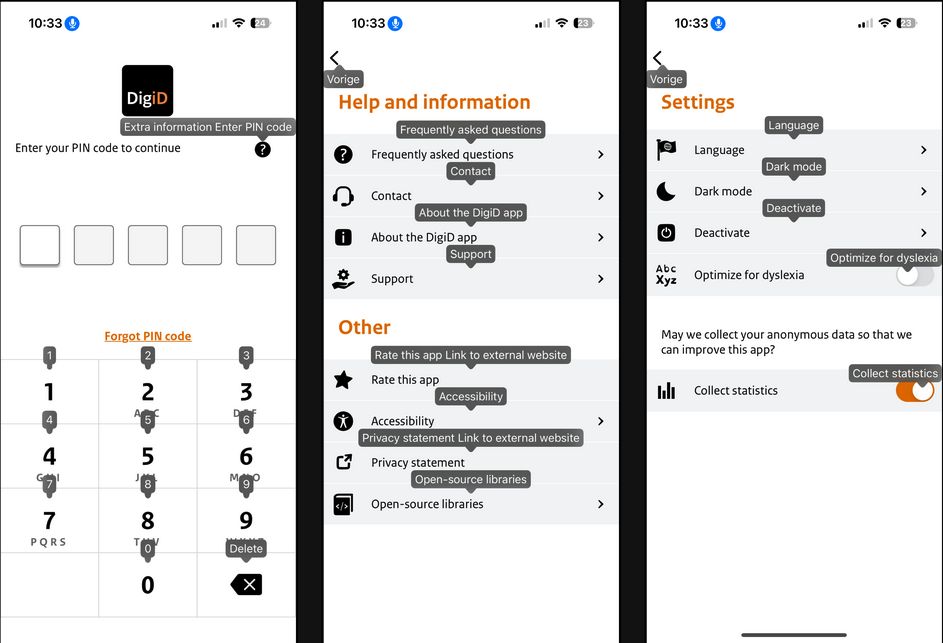

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | contentDescription | Flexible | |
| iOS | accessibilityLabel | Flexible | |
| Flutter | semanticsLabel | Flexible | |
| React Native | accessibilityLabel | Flexible | |
| Xamarin | AutomationProperties.Name | Flexible | |
| Web | aria-label | Flexible |
5. Role
Apps should provide an accessible role for elements, to ensure users of assistive technologies know their intent.
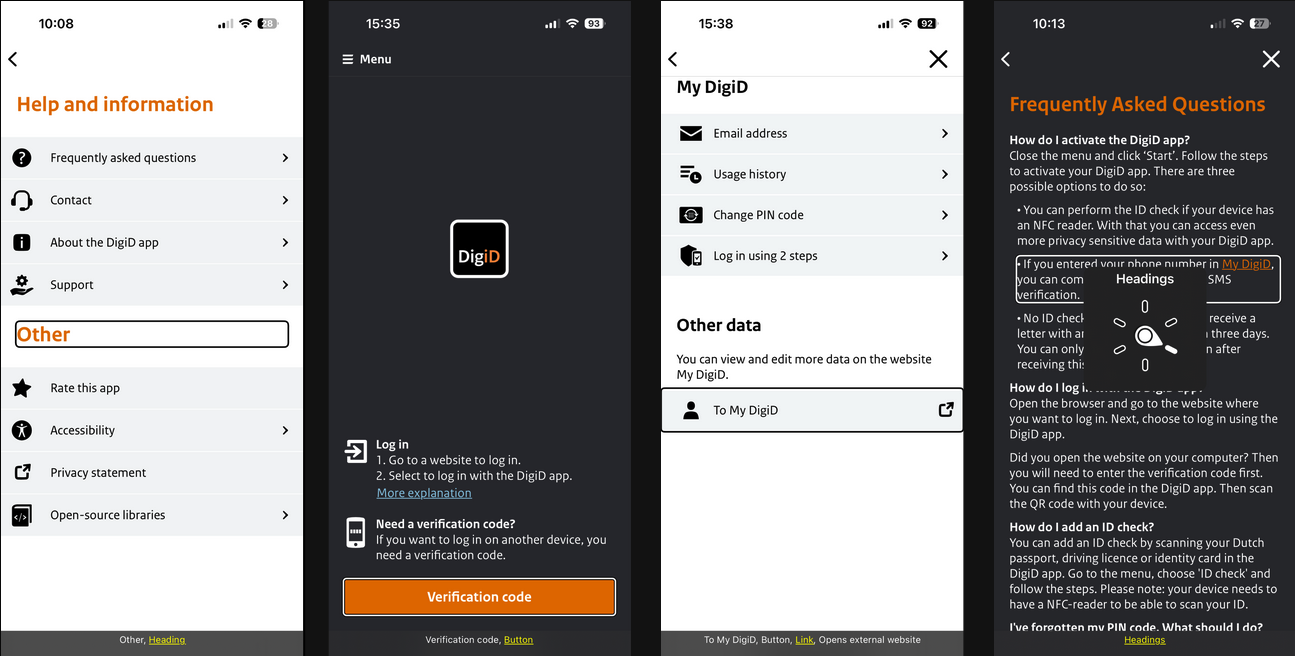

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | setRoleDescription or setClassName | Custom roles | |
| iOS | accessibilityTraits | No custom roles | |
| Flutter | Semantics → role | No custom roles | |
| React Native | accessibilityRole | No custom roles | |
| Xamarin | SemanticEffect → setDescription | 3rd party library, uses contentDescription | |
| Web | role / aria-roledescription | Custom roles |
6. Value
Apps should provide an accessible value for elements, to ensure users of assistive technologies know their current value.
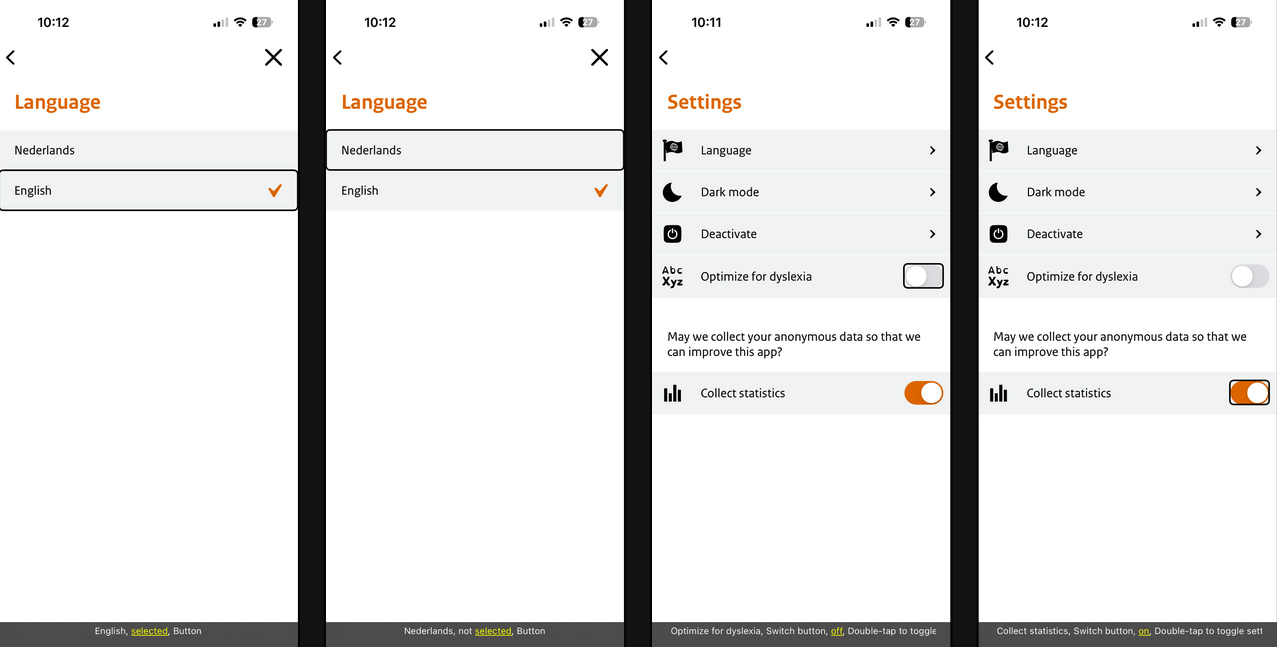

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat | Limited types | |
| iOS | accessibilityValue | Flexible | |
| Flutter | Semantics → value | Flexible | |
| React Native | accessibilityValue | Flexible | |
| Xamarin | Not supported | Can’t set accessibility value | |
| Web | aria-valuenow / aria-valuetext | Flexible |
7. State
Apps should provide an accessible state for elements, to ensure users of assistive technologies know their current state.
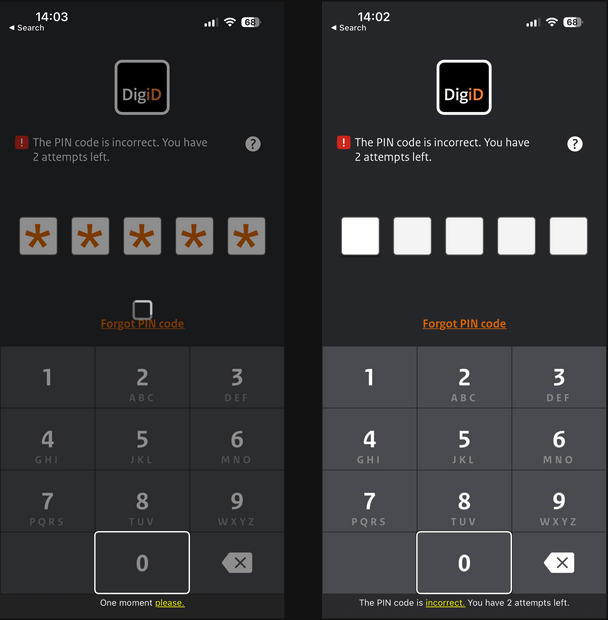

| Framework | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | setStateDescription and AccessibilityNodeInfoCompat | Flexible | Requires Android 11 (API 30) |
| iOS | accessibilityTraits | No custom states | |
| Flutter | Semantics → state | No custom states | |
| React Native | accessibilityState | No custom states | |
| Xamarin | Not supported | Can’t set accessibility state | |
| Web | ARIA states, e.g. aria-selected | Extensive |
8. Focus order
Apps should provide a logical focus order, allowing users of assistive technologies to navigate efficiently.
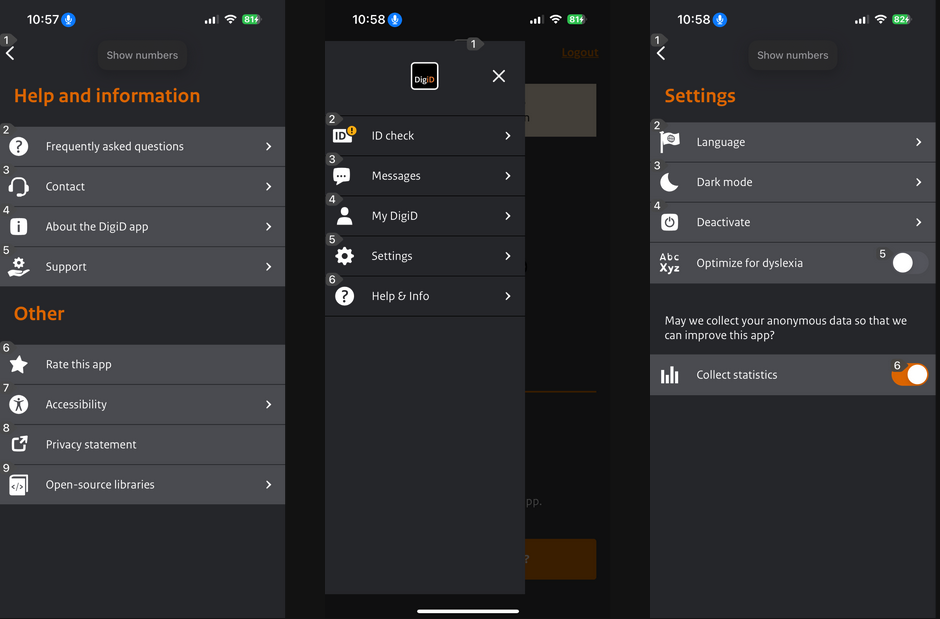

| Platform | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | setAccessibilityTraversalBefore/After | Single adjustment | Two API’s |
| iOS | accessibilityElements | Full control | Keep array up-to-date |
| Flutter | SemanticsSortKey | Flexible | |
| React Native | Not supported | Can’t change accessibility order | |
| Xamarin | TabIndex and IsTabStop | Flexible | Keep indices up-to-date |
| Web | tabindex | Flexible | Keep indices up-to-date |
9. Focus change
Apps might need to move the focus of assistive technologies, to ensure users end up at the right element.

| Platform | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | AccessibilityEvent → TYPE_VIEW_FOCUSED | ||
| iOS | UIAccessibility.Notification → screenChanged or layoutChanged | Two types | |
| Flutter | FocusSemanticEvent | ||
| React Native | setAccessibilityFocus | ||
| Xamarin | SemanticExtensions → SetSemanticFocus | 3rd party library | |
| Web | tabindex / focus() | Multiple options |
10. Status messages
Apps should communicate major interface changes to assistive technologies, to ensure users know what's going on.


| Platform | Feature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android | AccessibilityEvent → TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT or View.announceFor Accessibility | Two options | |
| iOS | UIAccessibility.Notification → announcement | Simple | |
| Flutter | SemanticsService → announce | Easy | |
| React Native | AccessibilityInfo → announceForAccessibility | Easy | |
| Xamarin | SemanticExtensions → Announce | Easy | 3rd party library |
| Web | aria-live | Less control |
Conclusion
So, which framework do we recommend for accessible app development? Native frameworks provide the best accessibility support.
It may not be feasible to maintain two codebases and two development teams. Fortunately, cross-platform frameworks are expanding their support for accessibility features.
But beware, when using cross-platform frameworks you may not be able to access certain accessibility features due to layers of abstraction. If you want to develop the most accessible app, native is always the best choice.
| Framework | Score | Verdict |
|---|---|---|
| Android | 100% | Full support |
| iOS | 100% | Full support |
| Web | 100% | Full support |
| Flutter | 100% | Full support |
| React Native | 90% | Good support, lacks accessibility order change |
| Xamarin | 50-80% | Mediocre support, lacks accessibility state/value, requires 3rd party libraries |
Check our in-depth documentation for further guidance:
- Learn about Android accessibility
Android accessibility
Android has an accessibility layer that helps users to navigate their Android devices more easily. By integrating accessibility features, you can improve your app's usability, particularly for users with disabilities.
- Learn about iOS accessibility
iOS accessibility
iOS has built-in accessibility features, accessibility APIs, and developer tools which provide an extraordinary opportunity to deliver a superior mobile experience to every user, including those with disabilities.
- Learn about Flutter accessibility
Flutter accessibility
Flutter is committed to supporting developers in making their apps more accessible. It has built-in support for accessibility features provided by the underlying operating system.
- Learn about React Native accessibility
React Native accessibility
React Native has accessibility APIs which let your app accommodate all users. You can integrate apps with assistive technologies like the screen readers VoiceOver and TalkBack.
- Learn about .NET MAUI accessibility
.NET MAUI accessibility
.NET MAUI has built-in semantics for accessibility and includes support for accessibility features, allowing developers to build inclusive apps.
- Learn about Xamarin accessibility
Xamarin accessibility
Xamarin has features to create apps which work well with accessibility features such as large type, high contrast, zoom in, screen reading, visual or haptic feedback cues, and alternative input methods.
Credits
This article is an adapted version of the talk Jan Jaap de Groot gave at the #id24 conference on 21 September 2023. You can watch the recording for more details.







